Type 1 diabetes: Managing tricky meal combinations. Presented by Dr Carmel Smart, PhD, APD
Carbohydrate counting for mealtime insulin dose calculation is the current standard of care across diabetes centres nationally and internationally. Clinical guidelines now recommend also dosing for fat and protein. In her presentation, Carmel explains best clinical practice regarding:
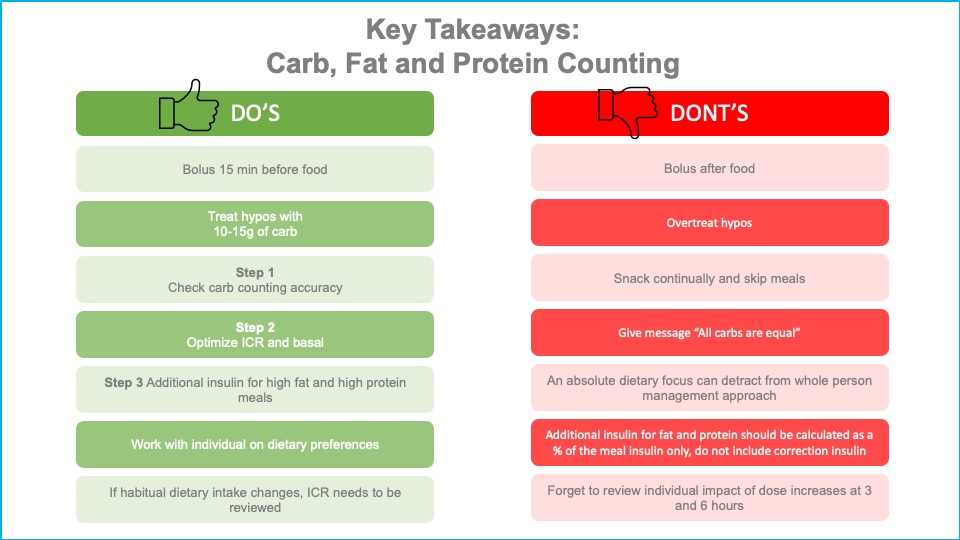
1. Counting carbohydrates
- Carbohydrate should be counted accurately to within 10-15g
- A consistent method of carbohydrate counting should be used
- Carbohydrate counting accuracy should be revised regularly with clients
- Choosing lower GI foods assists with BG management
2. Multiple daily injections and Pump therapy. An explanation of the insulin dosing strategies which work best for fat and protein.
- The insulin to carbohydrate ratio (ICR) and basal should be optimised to determine the impact of fat and protein
- Teach clients how to identify high protein and high fat meals that may cause delayed rise in BGLs
- Pump therapy : High fat, high protein meals
- Start with additional 20% ICR and grade up in 10% increments to 40% more
- Give dose as extended bolus (split 60:40) over 2-3 hrs
- MDI : High fat, high protein meals
- Start with additional 10%- 25% ICR and give all upfront.
- If hypo at 1-2 hours, split dose with additional insulin 60 min post- meal.
- Splitting the dose or using regular insulin does not usually confer advantage
3. Common meal and BG monitoring behaviours in people achieving target BGLs
- They monitor BG frequently with correction at meals of above target BGLs
- They have multiple (four or more) doses/day of pre-prandial insulin with food
- Insulin is administered for all snacks >10-15g Carb)
- They have a regular mealtime structure and routine
- They consider the impact of all macronutrients on insulin dose and delivery
- They understand their individual BG responses to foods

Dr Carmel Smart is recognised internationally as an authority on nutrition and type 1 Diabetes. Her accomplishments include being a lead author of the American Diabetes Association Clinical Nutrition Guidelines and a co-author of the International Society of Paediatric and Adolescent Diabetes Preschool Guidelines. She has published widely.
Carmel works as a Senior Specialist Diabetes Dietitian at the John Hunter Children’s Hospital in Newcastle Australia. This area of NSW has the highest rate of type 1 diabetes in Australia. With the team at John Hunter, she has developed a program for children who have type 1 diabetes which has transformed the lives of thousands of young people. The program includes intensive insulin therapy, diabetes education, dietary advice and psychological support, and the results are an incredible 83 per cent of their clients have achieved target glycaemia.
To register for the presentation and associated documents including the assessment quiz click here